Hydrogel Actuators and Miniature Soft Robots
For detailed information, please refer to the dissertation and the published paper in Advanced Materials journal.
Motivation and Goals
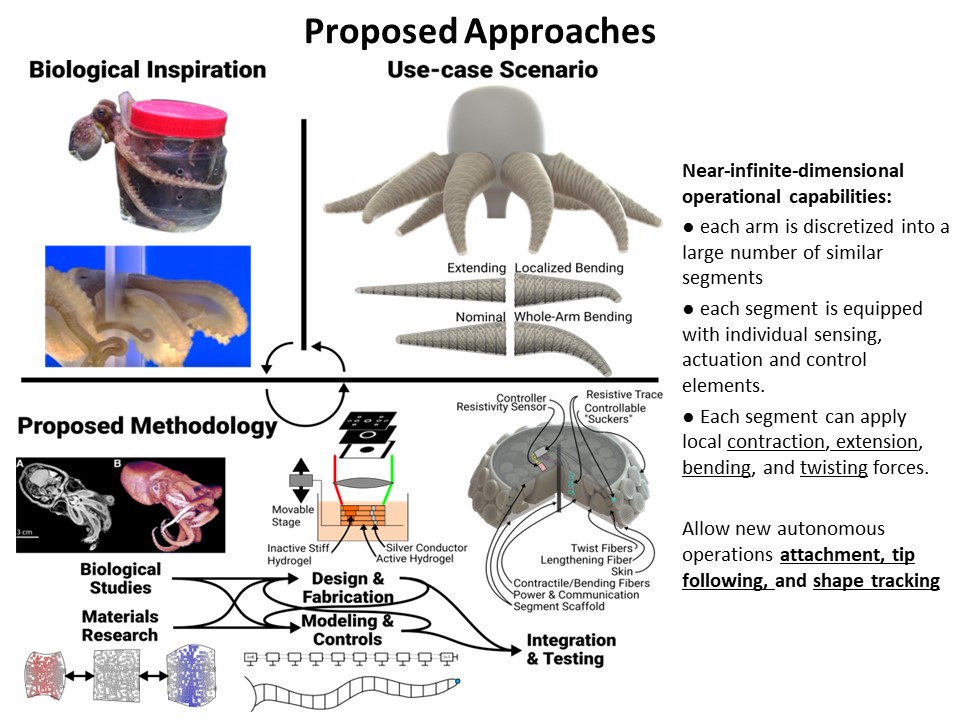
Why Soft Robots
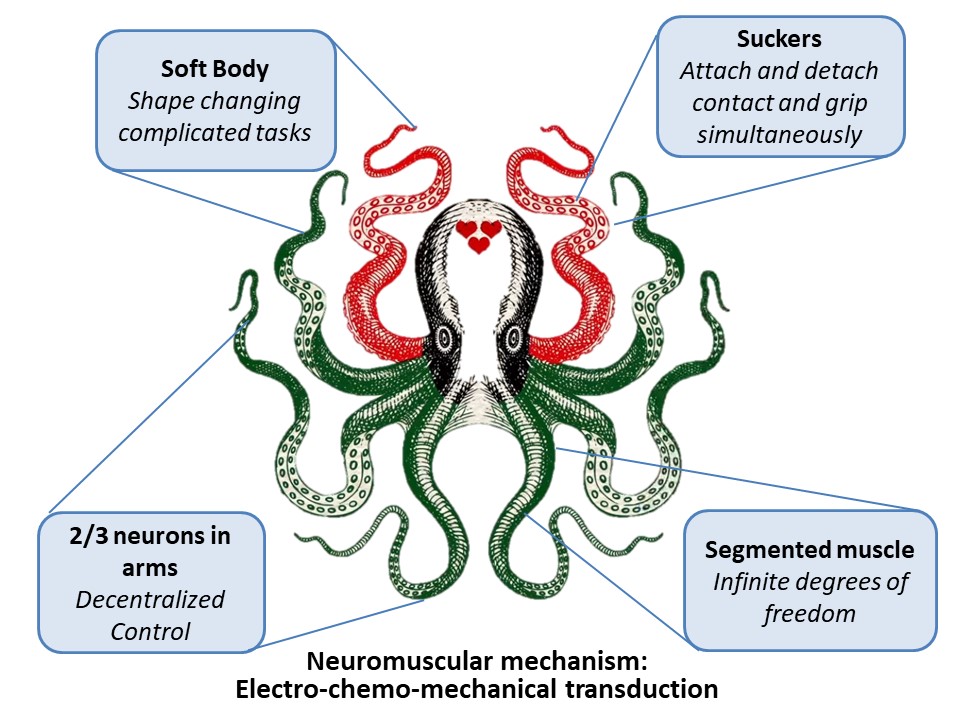
To answer this question, click on the image below to see how biological soft organism inspired this project.
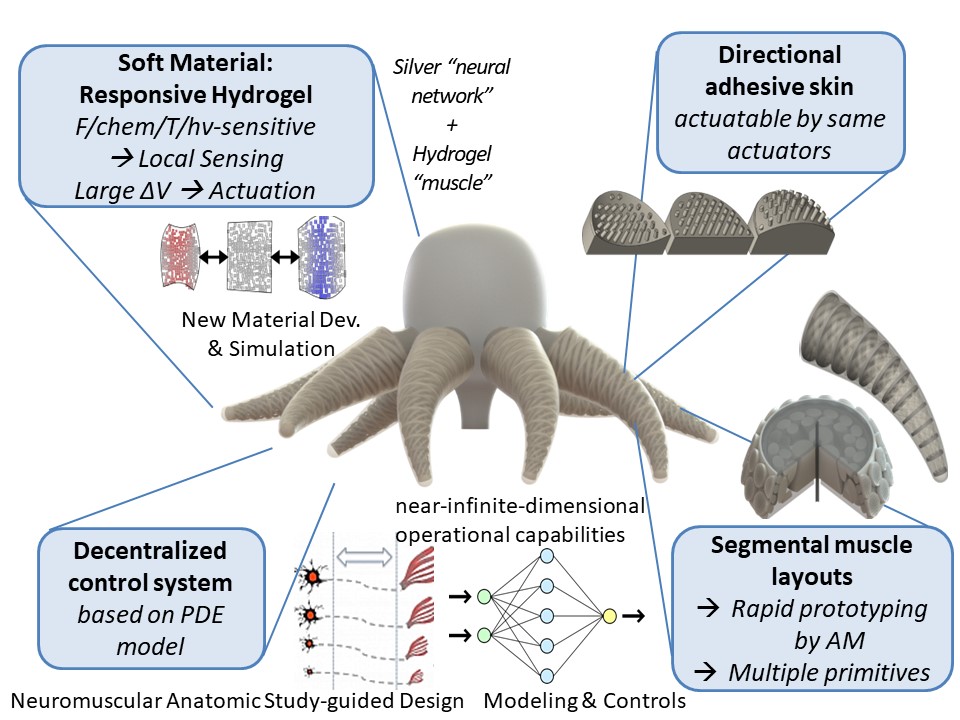
Achievemnts
Multiple soft robot platforms are developed using this methodology. This project resulted in top tier journal publications and patent applications.
Miniature Soft Robotic Manipulator
- Uses modular design. Each module is called a Voxel
- Voxels in this case are active, meaning they have a resistor inside to heat them up and the hydrogel responds to temperature changes.
- Scalable. Voxels can be added per demand
- High number of degrees of freedom. This results in ultra-redundant robots that can adapt to the environment and perform task that are unprecedented.
Passive Soft Manipulators
- The type of motion is embedded in the structure of the manipulators and is fixed.
- Voxels in this case are passive meaning they respond as the surrounding water temperature changes.
- Useful for .
Untethered Miniature Soft Robotic
- Uses 8 Voxels (2 for each leg)
- Light weight; only 20g including battery and electronics.
- Useful in underwater exploration and data collection.
-
—
by